Arthritis Of Foot & Ankle
By Isaac Tabari
NYC Podiatrists Treat Arthritis of the Foot & Ankle
Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in our country. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." Although arthritis of the feet cannot be cured, it can be treated by foot doctors. There are many treatment options available. It is important to start treatment early so that relief can begin as soon as possible. With treatment, people with arthritis are able to manage pain, and stay active, often without surgery.
Types of Arthritis affecting foot and ankle
There are three types of arthritis that may affect your foot and ankle.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis, also known as degenerative or "wear and tear" arthritis, is a common problem for many people after they reach middle age. Over the years, the smooth, gliding surface covering the ends of bones (cartilage) becomes worn and frayed. This results in inflammation, swelling, and pain in the joint. Osteoarthritis progresses slowly and the pain and stiffness it causes worsens over time. Many factors increase your risk for developing osteoarthritis. Because the ability of cartilage to heal itself decreases as we age, older people are more likely to develop the disease. Other factors that increase the risk are obesity and family history of the disease.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Unlike osteoarthritis which follows a predictable pattern in certain joints, rheumatoid arthritis is a system-wide disease. It is an inflammatory disease where the patient's own immune system attacks and destroys cartilage. The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not known. Although it is not an inherited disease, researchers believe that some people have genes that make them more susceptible. There is usually a "trigger," such as an infection or environmental factor, which activates the genes. When the body is exposed to this trigger, the immune system begins to produce substances that attack the joint. This is what may lead to the development of rheumatoid arthritis.
Gouty Arthritis
Gout is another form of arthritis that also leads to foot complications. Excess uric acid crystals collect in and around the joints of the big toe. The big toe joint is commonly the focal point due to the stress and pressure it experiences during walking and other weight bearing activities. This often leads to severe pain in the big toe. Men are more likely to develop gouty arthritis than women.
Post-Traumatic Arthritis
Post-traumatic arthritis can develop after an injury to the foot or ankle. This type of arthritis is similar to osteoarthritis and may develop years after a fracture, severe sprain, or ligament injury. Fractures - particularly those that damage the joint surface - and dislocations are the most common injuries that lead to this type of arthritis. An injured joint is about seven times more likely to become arthritic, even if the injury is properly treated. In fact, following injury, your body can secrete hormones that stimulate the death of your cartilage cells.
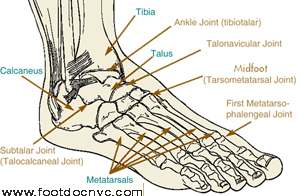
The joints most commonly affected by arthritis in the lower extremity include:
- The ankle
- The three joints of the hindfoot
- The midfoot
- The great toe. This is also the area where bunions usually develop.
Common Arthritis Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of arthritis of the foot vary, depending on which joint is affected. Common symptoms include:
- Pain or tenderness
- Stiffness or reduced motion
- Swelling
- Difficulty walking due to any of the above
Diagnosis
Your NYC podiatrist / foot doctor will base a diagnosis using your medical history, symptoms, a physical examination, and additional tests.
A medical history is important to understand more about the problem. Your foot doctor / podiatrist will want to know when the pain started and when it occurs. Is it worse at night? Does it get worse when walking or running? Is it continuous, or does it come and go? He will want to know if there was a past injury to the foot or ankle. If so, your podiatrist will discuss your injury, when it occurred, and how it was treated. Your foot doctor will want to know if the pain is in both feet or only in one foot, and where it is located exactly. Footwear will be examined, and any medications will be noted.
One of the tests performed by a foot doctor during the physical examination is the gait analysis. This shows how the bones in the leg and foot line up with walking, measures stride, and tests the strength of the ankles and feet. X-rays can show changes in the spacing between bones or in the shape of the bones themselves. Weight-bearing X-rays are the most valuable additional test in diagnosing the severity of arthritis. A bone scan, computed tomographic (CT) scan, or magnetic resonance image (MRI) may also be used in the evaluation.
Treatments
Depending on the type, location, and severity of the arthritis, there are many types of treatment available.
Non-surgical treatment options include:
- Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications to reduce swelling
- Shoe inserts (orthotics), such as pads or arch supports
- Custom-made shoe, such as a stiff-soled shoe with a rocker bottom
- An ankle-foot orthosis (AFO)
- A brace or a cane
- Forefoot supports such as gel toe caps, gel toe shields, gel toe straighteners and others can often provide relief.
- Physical therapy and exercises
- Weight control or nutritional supplements
- Medications, such as a steroid medication injected into the joint
Surgical treatment options:
If arthritis doesn't respond to nonsurgical treatment, surgical treatment might be considered. The choice of surgery will depend on the type of arthritis, the impact of the disease on the joints, and the location of the arthritis. Sometimes more than one type of surgery will be needed.
Surgery performed for arthritis of the foot and ankle include
Arthroscopic Debridement
Arthroscopic surgery may be helpful in the early stages of arthritis. A flexible, fiberoptic pencil-sized instrument (arthroscope) is inserted into the joint via small incisions through the skin. The arthroscope is fitted with a small camera and lighting system, as well as various instruments. The camera projects images of the joint on a television monitor. This enables the surgeon to look directly inside the joint and identify the problem areas. Small instruments at the end of the arthroscope, such as probes, forceps, knives, and shavers, are used to clean the joint area of foreign tissue, inflamed tissue that lines the joint, and bony outgrowths (spurs).
Arthrodesis (fusion of the joints)
Arthrodesis fuses the bones of the joint completely, making one continuous bone. The foot surgeon uses pins, plates and screws, or rods to hold the bones in the proper position while the joint(s) fuse. If the joints do not fuse (nonunion), this hardware may break. A bone graft is sometimes needed if there is bone loss. The foot surgeon may use a graft (a piece of bone, taken from one of the lower leg bones or the wing of the pelvis) to replace the missing bone. This surgery is typically quite successful. A very small percentage of patients have problems with wound healing. These problems can be addressed by bracing or additional surgery. The biggest long-term problem with fusion is the development of arthritis at the joints adjacent to those fused. This occurs from increased stresses applied to the adjacent joints.
Arthroplasty (replacement of the affected joint).
In arthroplasty, the damaged ankle joint is replaced with an artificial implant (prosthesis). Although not as common as as total hip or knee joint replacement, advances in implant design have made ankle replacement a feasible option for many people. In addition to providing pain relief from arthritis, ankle replacements offer patients better mobility and movement compared to fusion. By allowing motion at the formerly arthritic joint, less stress is transferred to the adjacent joints. Less stress results in reduced occurrence of adjacent joint arthritis. Ankle replacement is most often recommended for patients with: advanced arthritis of the ankle, destroyed ankle joint surfaces and an ankle condition that interferes with daily activities.
***This material is only provided as helpful information and not as medical advice and you should consult with your foot doctor or another medical doctor for a professional diagnosis. ***
For more information on foot and ankle podiatry services and to make an appointment with best NYC podiatrist - foot doctor, please call us at (212) 288-3137 or click below to make an appointment:

|