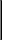NY Pediatric Podiatrist - Children's Foot Doctor
By Isaac Tabari
VIDEO: Learn about NYC's Pediatric Podiatrist and Get Explanation of Children's Foot Disorders
Learn about NYC's Pediatric Podiatrist and Explanation of Children's Foot Disorders from NYC Podiatry Center of Excellence.
Dr. Isaac Tabari, pediatric podiatrist strongly believes in the need for foot exams and gait exams as part of the annual pediatric well care checkup.
He offers complete care for any age and cutting-edge techniques to treat foot and ankle diseases, injuries and other disorders that may be slowing your child down. It's very important to begin foot care at a very young age because feet carry people for their entire lives. Dr. Tabari is an expert in children's foot conditions. Children can be affected by foot conditions such as
- plantar warts (plantar verrucae)
- fungal nails (onychomychosis)
- intoeing and outoeing
- heel pain in children
- tibial torsion
- metatarsus adductus
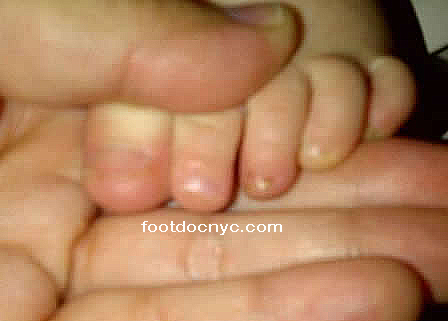
- ingrown nails
- flat feet
- sport injuries
- equinovarus
Neglecting foot health invites problems in other parts of the body, such as the legs and back. The child with troublesome feet walks awkwardly and usually has poor general posture. As a result, the growing child may become shy, introverted, and avoid athletics and social functions. Consultation with a New York podiatrist can help to resolve these related problems.
Although a lot of companies profess that children should be in softer shoes, as a podiatric doctor, I know that new walkers need support and protection. A child's foot needs to be maintained in proper biomechanical alignment and a soft shoe just does not provide this. Our own research based on our patient success stories tells us that children need to be in harder shoes that provide support.
Children's Feet - General Information
Most toddlers toe-in or toe-out because of a slight rotation (twist), of the upper or lower leg bones. Tibial torsion, the most common cause of in-toeing, occurs when the lower leg bone (tibia) tilts
The Human foot is one of the most complicated parts of the body - it has 26 bones, and has ligaments, muscles, blood vessels and nerves. The feet of a young child are soft and pliable; abnormal pressure can cause deformities. A child's feet grows rapidly during the first year, reaching almost half their adult foot size. Podiatrist, consider the first year to be the most important in development.
Tips to help foot development occur normally:
Provide exercise; lying uncovered provides kicking and other related motions which prepare the feet for weight bearing.
Change the baby's position several times a day.
Look at your baby's feet often if you notice something that does not look normal to you, ask your family physician or podiatrist.
Cover the baby's feet loosely; tight covers restrict movement.
Growing up:
While children's feet continue to grow and develop, it may be necessary to change shoe and sock size every few months. Improper footwear can aggravate preexisting conditions. Shoes or other footwear should never be handed down.
The feet of young children are often unstable because of muscle problems which make walking difficult or uncomfortable. A thorough examination by a podiatrist may detect an underlying defect or condition which may require immediate treatment or consultation with another specialist.
The American Podiatric Medical Association has long known of the high incidence of foot defects among the young and recommends foot health examinations for school children on a regular basis.
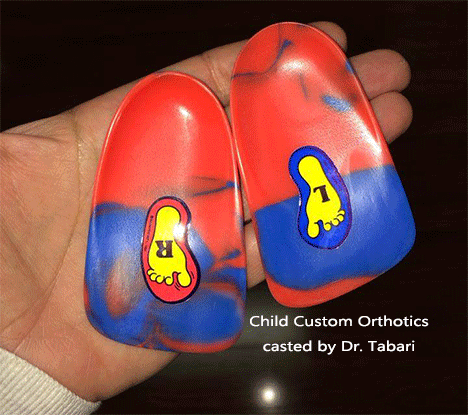
Child Foot Conditions: Plantar Warts in Kids
The human papillomavirus (HPV) causes hard growths on the soles of children's feet called plantar warts. They are common in children because they frequently have scrapes and cuts through which the HPV virus enters the body.
Warts come in many different sizes, colors, and shapes. Although most warts are painless, a wart on the bottom of the foot may really hurt. It may feel like the child has a stone in the shoe.
Children may benefit from treatment if they have painful, uncomfortable or multiplying plantar warts. We use a variety of conservative and safe treatments for this condition.
Fungal Nails in Children
Many cases of pediatric onychomychosis (children's fungal toenails) involve an underlying nail problem which results in a nail deformity. This in turn makes the toe nail susceptible to fungal nail infections. Some of these nail problems include conditions such as psoriasis and ectodermal dysplasia, or congenital problems, among others. Another common reason for infections is nail trauma that caused subungual hematoma and damage to the nail matrix. If a child has chronic ingrown nails, this can also cause deformity of nail which in turn can cause fungal infections.
Our primary approach to treatment is to first determine what has caused a fungal nail infection. We need to first see whether the underlying condition can be corrected. Then we treat fungal nails in children using conservative and proven methods.
In-toeing / Out-toeing
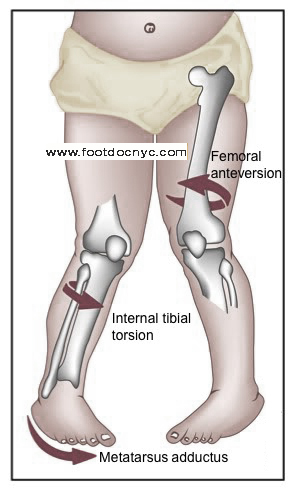
Most toddlers toe-in or toe-out because of a slight rotation (twist), of the upper or lower leg bones. Tibial torsion, the most common cause of in-toeing, occurs when the lower leg bone (tibia) tilts inward. If the tibia tilts outward, a child will toe-out. When the thighbone, or femur, is tilted, the tibia will also turn and give the appearance of intoeing or outtoeing. The medical term for this is femoral anteversion. In-toeing can also be caused by metatarsus adductus, a curving of the foot that causes toes to point inward.
The reason some kids develop gait abnormalities is unclear, but studies have shown that a family history of in-toeing or out-toeing plays a role. So, if you toed-in or toed-out as a child, there's a chance that your child could develop the same tendency.
Some experts also believe that, the position of the fetus in the womb during pregnancy could also lead to in-toeing or out-toeing.
As a fetus grows, some of the bones have to rotate slightly to fit into the small space of the womb. In many cases, these bones are still rotated to some degree for the first few years of life. Many times this is most noticeable when a child learns to walk, because if the tibia or femur is tilted at an angle, the feet are, too.
Pediatric Heel Pain
What is pediatric heel pain? Heel pain is a common childhood complaint. That doesn't mean, however, that it should be ignored, or that parents should wait to see if it will "go away." Heel pain is a symptom, not a disease. It's a warning sign that a child has a condition that deserves your and foot doctor's attention.
Calcaneal apophysitis
Also known as Sever's disease, this is the most common cause of heel pain in children. Although not a true "disease," it is an inflammation of the heel's growth plate due to muscle strain and repetitive stress, especially in those who are active or obese. This condition usually causes pain and tenderness in the back and bottom of the heel when walking and the heel is painful when touched. It can occur in one or both feet.
Overuse syndromes
Because the heel's growth plate is sensitive to repeated running and pounding on hard surfaces, pediatric heel pain often reflects overuse. Children and adolescents involved in soccer, track, or basketball are especially vulnerable. One common overuse syndrome is Achilles tendonitis. This inflammation of the tendon usually occurs in children over the age of 14. Another overuse syndrome is plantar fasciitis, which is an inflammation of the band of tissue (the plantar fascia) that runs along the bottom of the foot from the heel to the toes.
Fractures
Sometimes heel pain is caused by a break in the bone. Stress fractures-hairline breaks resulting from repeated stress on the bone-often occur in adolescents engaged in athletics, especially when the intensity of training suddenly changes. In children under age of 10, another type of break-acute fractures-can result from simply jumping 2 or 3 feet from a couch or stairway.
Diagnosis
To diagnose the underlying cause of your child's heel pain, the podiatric surgeon will first obtain a thorough medical history and ask questions about recent activities. The surgeon will also examine the child's foot and leg. X-rays are often used to evaluate the condition and in some cases the surgeon will order a bone scan, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) study, or a computerized tomography (CT or CAT) scan. Laboratory testing may also be ordered to help diagnose other less prevalent causes of pediatric heel pain .
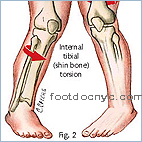
Tibial Torsion / Intoeing
Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shin bones (these are bones located between the knee & ankle). The portion of the leg from knee down to ankle is turned inward. Tibial torsion causes your child's feet to turn inward, or have a "pigeon-toed" appearance, often-times seen in young children.
When your toddler starts to learn to walk, tibial torsion can create an intoeing appearance, which makes the legs look bowed. This bowed leg stance helps children be balanced. If they try to stand with their feet closer together or feet turned out, the childrens' balance is not as steady and causes them to trip. A skilled podiatrists will observe whether the legs will straighten naturally or whether a child will need to wear corrective braces. Surgery is only necessary in severe cases of tibial torsion.
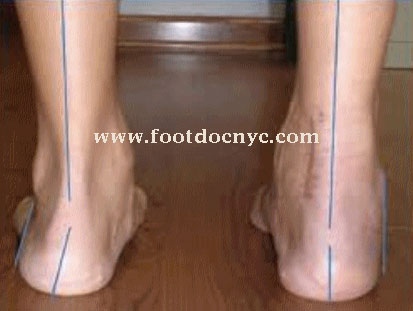
Flat Feet in Children
Flatfoot is a common foot shape that has another medical term: pronated foot. Commonly, when a person with flatfoot stands on his/her feet, the foot seems to lie flat on the ground and the arch in the middle of the foot disappears.
Almost all children are born with flatfoot. Statistics show that 80% to 90% of babies born in North America have flatfoot. Studies in other countries have found similar numbers. Most of these babies have flexible flatfoot.
Children often outgrow flatfoot naturally. This condition is not painful, causes no disability and does not need any treatment. It always affects both feet.
Our office's goal is to provide the child's foot proper alignment - and that's where orthotics come in. Pronation (flat foot) needs to be limited as early as possible when
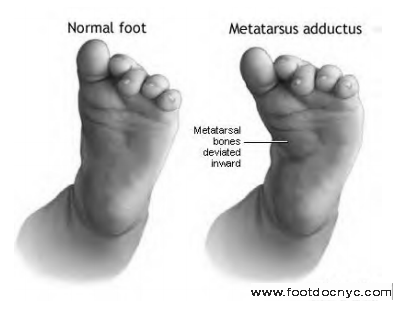
Metatarsus Adductus
Metatarsus adductus, also known as metatarsus varus, is a common foot deformity that causes the front half of the foot to turn inward.
At birth, the foot may be "flexible" (parents or doctor can straighten the foot to a degree by hand manipulation) or "non-flexible" (the foot can't be straightened by hand).
This deformity occurs in about one of every 1,000-2,000 live births.
Babies with metatarsus adductus are at an increased risk for developmental dysplasia of the hip.
Treatment should be started by a skilled foot doctor immediately, regardless of how much the forefoot turns inward, as this improves your child's prognosis. But babies born with metatarsus adductus rarely need treatment since this condition often corrects itself as the baby grows.
Surgery is rarely needed and is performed for only the most severe cases of this condition.
***This material is only provided as helpful information and not as medical advice and you should consult with your foot doctor or another medical doctor for a professional diagnosis. ***
For more information on child foot treatments and to make an appointment with NYC's top pediatric podiatrist - foot doctor, please call us at (212) 288-3137 to schedule your appointment, click below to book an appointment:

|